- To receive a stimulus
- Transmission of a stimulus to a central “brain”
- Interpretation and analysis of the stimulus
- Proper response by effectors
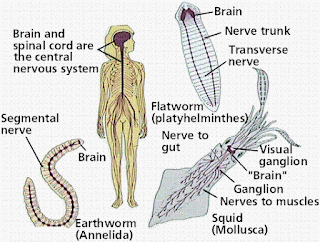
with the evolution of a complex nervous system and bilateral symmetry, cephalization (formation of a head) has taken Place, and the ganglia in the head became large enough to called a brain, which is the main nervous control center of the body.
there are several type of neural organization
in the animal kingdom. In the unicellular from, the single cell functions both
as receptor and effector, there are no structural specializations.
In the cnidarians (Coelenterates) specialized cell are found in the body which functions as neurons or nerve cells. These neurons are multipolar and non-myelinated and organized in the from of a diffused nerve net. This nerve network is located in the body wall (mesoglia)
In platyhelminthes a more complex nervous system basically resembling a ladder is present. In its basic from, a nerve ring or pair of cerebral ganglia is present in the anterior end of the body. The neurons of cerebral ganglia is present in the anterior end of the body. The neurons of this nervous system are non-myelinated. From this nerve ring two lateral solid nerve cords originate and passes towards the posterior end of the body. These two lateral nerve cords are connected by several transverse nerves which give a ladder like structure. Therefore platyhelminthes have a rudiment of a central nervous (brain and nerve cords) and peripheral nervous systems (transverse nerves).